Country:
Region:
City:
Latitude and Longitude:
Time Zone:
Postal Code:
IP information under different IP Channel
ip-api
Country
Region
City
ASN
Time Zone
ISP
Blacklist
Proxy
Latitude
Longitude
Postal
Route
Luminati
Country
Region
nor
City
touques
ASN
Time Zone
Europe/Paris
ISP
K-NET SARL
Latitude
Longitude
Postal
IPinfo
Country
Region
City
ASN
Time Zone
ISP
Blacklist
Proxy
Latitude
Longitude
Postal
Route
db-ip
Country
Region
City
ASN
Time Zone
ISP
Blacklist
Proxy
Latitude
Longitude
Postal
Route
ipdata
Country
Region
City
ASN
Time Zone
ISP
Blacklist
Proxy
Latitude
Longitude
Postal
Route
Popular places and events near this IP address

CERN
European research centre in Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 2536 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.23416667,6.05277778
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; French pronunciation: [sɛʁn]; Organisation européenne pour la recherche nucléaire), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 24 member states.

Large Electron–Positron Collider
Particle accelerator at CERN, Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 1930 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.235,6.045
The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) was one of the largest particle accelerators ever constructed. It was built at CERN, a multi-national centre for research in nuclear and particle physics near Geneva, Switzerland. LEP collided electrons with positrons at energies that reached 209 GeV. It was a circular collider with a circumference of 27 kilometres built in a tunnel roughly 100 m (300 ft) underground and passing through Switzerland and France.
Super Proton Synchrotron
Particle accelerator at CERN, Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 1740 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.235,6.0425
The Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) is a particle accelerator of the synchrotron type at CERN. It is housed in a circular tunnel, 6.9 kilometres (4.3 mi) in circumference, straddling the border of France and Switzerland near Geneva, Switzerland.
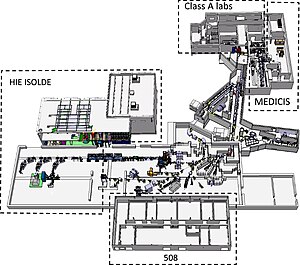
ISOLDE
Physics facility at CERN
Distance: Approx. 2156 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.23416667,6.04777778
The ISOLDE (Isotope Separator On Line DEvice) Radioactive Ion Beam Facility, is an on-line isotope separator facility located at the centre of the CERN accelerator complex on the Franco-Swiss border. Created in 1964, the ISOLDE facility started delivering radioactive ion beams (RIBs) to users in 1967. Originally located at the Synchro-Cyclotron (SC) accelerator (CERN's first ever particle accelerator), the facility has been upgraded several times most notably in 1992 when the whole facility was moved to be connected to CERN's ProtonSynchroton Booster (PSB).

ALICE experiment
Distance: Approx. 1507 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.25133333,6.02013889
ALICE (A Large Ion Collider Experiment) is one of nine detector experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. The experiment is designed to study the conditions that are thought to have existed immediately after the Big Bang by measuring the properties of quark-gluon plasma.

Intersecting Storage Rings
Particle accelerator at CERN, Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 1788 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.23472222,6.04305556
The ISR (standing for "Intersecting Storage Rings") was a particle accelerator at CERN. It was the world's first hadron collider, and ran from 1971 to 1984, with a maximum center of mass energy of 62 GeV. From its initial startup, the collider itself had the capability to produce particles like the J/ψ and the upsilon, as well as observable jet structure; however, the particle detector experiments were not configured to observe events with large momentum transverse to the beamline, leaving these discoveries to be made at other experiments in the mid-1970s. Nevertheless, the construction of the ISR involved many advances in accelerator physics, including the first use of stochastic cooling, and it held the record for luminosity at a hadron collider until surpassed by the Tevatron in 2004.

Satigny
Municipality in Geneva, Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 2559 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.21666667,6.03333333
Satigny (French pronunciation: [satiɲi]) is a municipality of the Canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It is the largest municipality of the canton by land area and the largest wine-producing municipality of the country. Its territory contains the majority of the Mandement area, a designated heritage site of national importance shared with the neighbouring municipalities of Russin and Dardagny.

Saint-Genis-Pouilly
Commune in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France
Distance: Approx. 751 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.2437,6.025
Saint-Genis-Pouilly (French pronunciation: [sɛ̃ ʒəni puji]; Arpitan: Sant-Genés-Polyi) is a commune in the Ain department within the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It is located in the Pays de Gex, at the foot of the Jura Mountains. Bordering the Swiss frontier, it is part of the cross-border area of Geneva.
Sergy, Ain
Commune in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France
Distance: Approx. 2276 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.252,5.999
Sergy (French pronunciation: [sɛʁʒi]; Arpitan: Sèrgi) is a commune in the Ain department in eastern France.
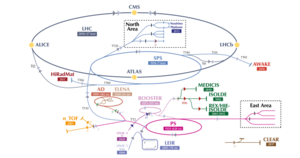
Antiproton Decelerator
Particle storage ring at CERN, Switzerland
Distance: Approx. 2058 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.23388889,6.04638889
The Antiproton Decelerator (AD) is a storage ring at the CERN laboratory near Geneva. It was built from the Antiproton Collector (AC) to be a successor to the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) and started operation in the year 2000. Antiprotons are created by impinging a proton beam from the Proton Synchrotron on a metal target.

Choully Castle
Swiss castle
Distance: Approx. 1795 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.223068,6.029759
Choully Castle is a castle in the municipality of Satigny of the Canton of Geneva in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.
Synchro-Cyclotron (CERN)
Particle and Nuclear Physics
Distance: Approx. 2559 meters
Latitude and longitude: 46.232976,6.052763
The Synchro-Cyclotron, or Synchrocyclotron (SC), built in 1957, was CERN’s first accelerator. It was in circumference and provided for CERN's first experiments in particle and nuclear physics. It accelerated particles to energies up to 600 MeV. The foundation stone of CERN was laid at the site of the Synchrocyclotron by the first Director-General of CERN, Felix Bloch.
Weather in this IP's area
overcast clouds
11 Celsius
10 Celsius
8 Celsius
11 Celsius
1026 hPa
86 %
1026 hPa
974 hPa
10000 meters
1.03 m/s
100 %
07:27:25
17:12:00

